Let’s start with a Story of Equifax depicted in the below Picture
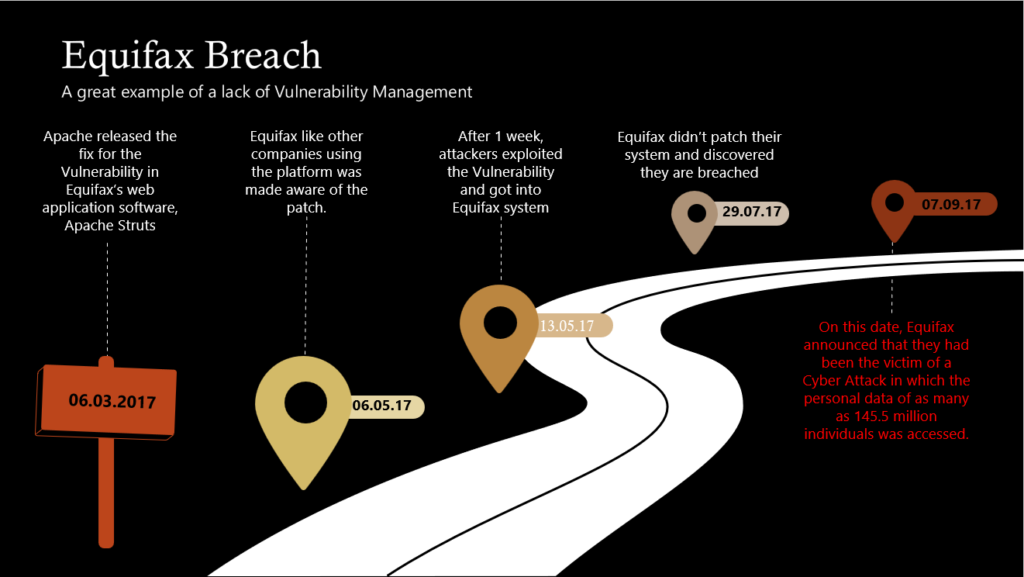
Although close to three months sounds like a long time to patch a critical vulnerability, Equifax isn’t even close to being the slowest company to patch systems against critical vulnerabilities. For instance, there are still plenty of systems in the wild that are susceptible to the EternalBlue exploits that enabled both NotPetya and WannaCry during the Summer of 2017. And while Equifax’s story sounds like chaos, it’s more often than not the reality for teams tasked with managing complex computing infrastructure.
Vulnerability Management
It is an ongoing process of identifying, classifying, prioritizing, mitigating, and remediating vulnerabilities across all the Enterprise components like, Servers, Networks, Databases, Applications and Endpoints. Typically, in an Enterprise environment Vulnerability Management requires multiple Teams involvement starting from Security Leadership, Infrastructure, Governance and Security Teams.
The below picture shows the complete Vulnerability Management Process Lifecycle

Before we understand the complete process, first we need to understand the difference between Vulnerability, Exploit, Threat and Risk.
A Vulnerability is a weakness or a loophole in an asset that can be exploited by one or many threats.
For e.g CVE-2017-0144 was a well-known Vulnerability found on Windows devices using SMBv1 protocol which allows a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via crafted packets, aka “Windows SMB Remote Code Execution Vulnerability.”
An Exploit is typically source code or a script used to take advantage of the Vulnerability.
For e.g Eternal Blue was the exploit which was used by attackers to take advantage of the SMBv1 Vulnerability (CVE-2017-0144).
A Threat is any action, that could disrupt, harm, destroy or take any adverse effect of the asset.
For e.g Wannacry/Not Petya Ransomware was the Threat which had used the Eternal Blue exploit to take advantage of the SMBv1 Vulnerability.
A Risk is what happens when a threat exploits a vulnerability. It’s a damage that could be caused by the open vulnerability being exploited by a threat.
For e.g The Risk of Wannacry/Not Petya was extremely high, because it can encrypt/destroy data.
Vulnerability Management Process
- Asset Prioritization – First Identify the Enterprise Assets and prioritize the asset based on Business Value. For e.g for Ecommerce Company their Ecommerce portal/system is the most important asset to protect whereas for Aviation Industry Online Reservation portal/system is an important asset. On the other hand, Domain Controllers, Exchange, Database, File Servers are the most critical asset to protect whereas a frontend Webserver could be treated as less critical server.
Result – You have successfully Identified the Most Critical Assets for your Organization which you have to protect at any cost.
- Correlate Threats
- Not all threats and Vulnerabilities have equal priority. Categorize the Vulnerabilities using CVSS( Common Vulnerability Scoring System).
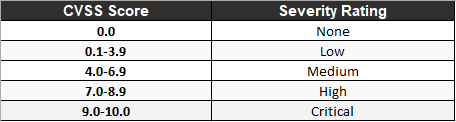
- Identify whether the Vulnerability is true or false positive.
- Whether any exploit code exist for Vulnerability and how dificult is to exploit this Vulnerability.
- Our primary goal is to protect the most critical assets.
- Identify threats, like Worms, Exploit, Wide-scale attacks or Zero-day attacks
- Correlate all threats with critical assets.
Result – You have successfully Prioritize the vulnerabilities with your assets in your organization.
- Risk Calculation
- Risk is union of
- Vulnerabilities
- Assets
- Threats
- Based upon the criticality of VAT, focus your resources on True Risk.
- What would be the Impact on Business if this Vulnerability were exploited.
- Are there any Security control in place to reduce the likelihood and/or impact of this vulnerability.
- Do the Risk Assessment using the below Qualitative Matrix
- Risk is union of

Result – You have successfully Identified and Calculated the Risk for your Organization.
- Remediation
- 100% remediation is technically not possible, for an Enterprise environment where we have thousands of Vulnerabilities identified by the time you remediate these thousands other thousands will pop up. So remediation should be on going process.
- Factor is the business impact costs + remediation costs.
- If the risk is greater than the cost – eliminate or mitigate the vulnerability
- If the risk is lower than the cost – accept or transfer the vulnerability
- Apply the Pareto Principle – 80/20 Rule
- 80% of your risk can be eliminated by addressing 20% of the issues.
- Assign the task to respective Asset Owners and Define a SLA (Service Level Agreement) for remediating the Vulnerabilities.
- Apply patches or fixes to remediate the Vulnerabilities.
Result – You have successfully either Remediated or Mitigated the Vulnerabilities for your Organization.
- Measure
- You can’t manage what you can’t measure.
- Know the current state of security metrics.
- Make someone accountable with timeline.
- A standard to quantify the risk.
- Dashboard view of Risk and Vulnerabilities across whole Organization.
- Remediation progress over time.
Result – You have successfully Measured the Risk and Vulnerabilities for your Organization for which you need to start working on.
Some of the most Renowned Vulnerability Management Vendors
♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥Thank You for Reading, See you in the next Blog♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥♥